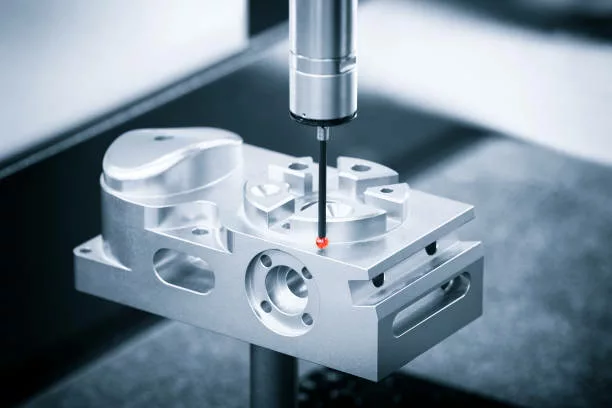
Coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) have long been the measurement standard technology in the manufacturing industry. However, the development of multi-sensor metrology has introduced a new dimension to component analysis, offering a more versatile and comprehensive approach to measurement and even greater levels of inspection for all industries. Multi-sensor metrology shines in its combination of contact and non-contact sensors, enabling comprehensive and efficient assessment of complex geometries, surface characteristics, and material properties.
What are the differences between CMM and Multi-sensor metrology systems?
CMM’s are a slow, complicated technology that rely on sensors having physical contact with the component. This not only limits their measurement capabilities but also increases the risk of damaging or moving delicate and flexible components during an inspection.
Multi-sensor metrology is a modern inspection technology that utilises a combination of sensors, including tactile probes, optical systems, and non-contact technologies, to provide a more comprehensive and efficient measurement experience. This synergistic approach ensures the best-suited sensor is used to capture particular dimensions, allowing for the capture of both complex geometric features and surface characteristics which enable a more detailed assessment of component quality.
CMM VS Multi-sensor metrology
| CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machines) | Multi-sensor metrology system | |
|---|---|---|
| Fast measurement | ||
| Utilisation of multiple sensors in a single program | ||
| High accuracy | ||
| Combine data from multiple sensors to produce comprehensive measurement reports | ||
| User-friendly software and interfaces | ||
| Small footprint on the shopfloor | ||
| Easily transportable to multiple locations on site | ||
| Accommodates a bespoke combination of sensors onto one machine to suit each companies needs, growing and adapting with the company | ||
| Measures a wide range of features on single part | ||
| High-quality inspection | ||
| Designed to measure complex and multi-dimensional parts | ||
| High reliability and repeatability | ||
| Increases efficiency | ||
| Risk of damaging the component |